
Brain Aneurysm
A bulge in a brain blood vessel that can rupture. Often treated with minimally invasive techniques.
Find out moreDr Jeremy Lynch MBChB MRCS FRCR is a London-based Consultant specialising in minimally invasive treatment of vascular conditions of the brain and spine. He is dual trained in neurointervention (endovascular neurosurgery or interventional neuroradiology) and diagnostic neuroradiology. His practice specialises in complex brain aneurysms, cerebral and spinal angiography, brain arteriovenous malformations, dural fistula, stroke, carotid stenosis, and pre-operative embolisation. He is the lead editor for the Oxford Specialist Handbook of Neurointervention.
Dr Lynch graduated in Medicine from the University of Bristol in 2007. After completing basic surgical training he specialised in interventional radiology and neuroradiology at leading London hospitals, followed by a competitive international fellowship in Toronto, where he was among the first in the world to gain experience in robotic endovascular techniques. He works in Kings College and Queens hospitals and the Wellington Hospital. He regularly authors peer-reviewed publications, is invited to speak at international conferences, and is an expert reviewer for major medical journals. Dr Lynch believes strongly in listening to patients and respecting their values and choices.







A bulge in a brain blood vessel that can rupture. Often treated with minimally invasive techniques.
Find out more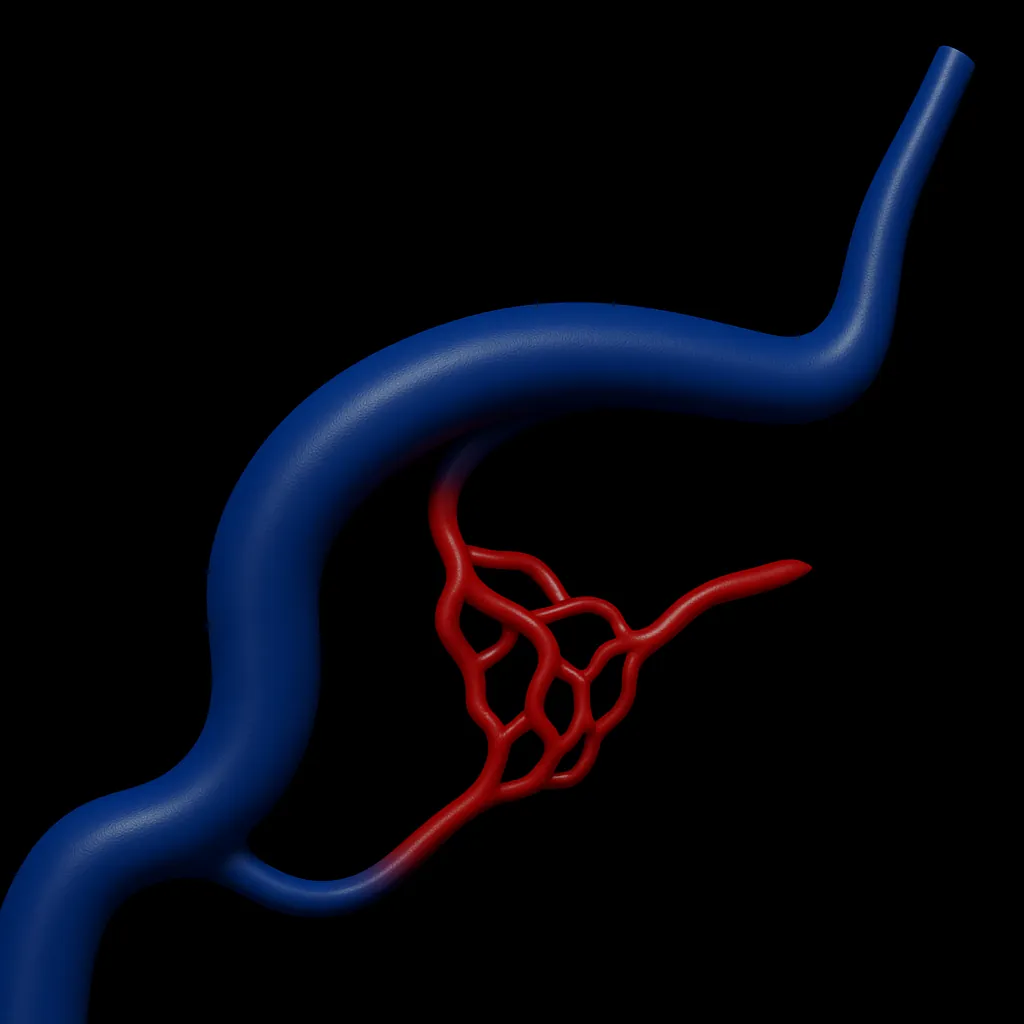
Abnormal artery to vein connections can affect brain function, hearing or vision. Treated using image-guided techniques to block the problem vessels.
Find out more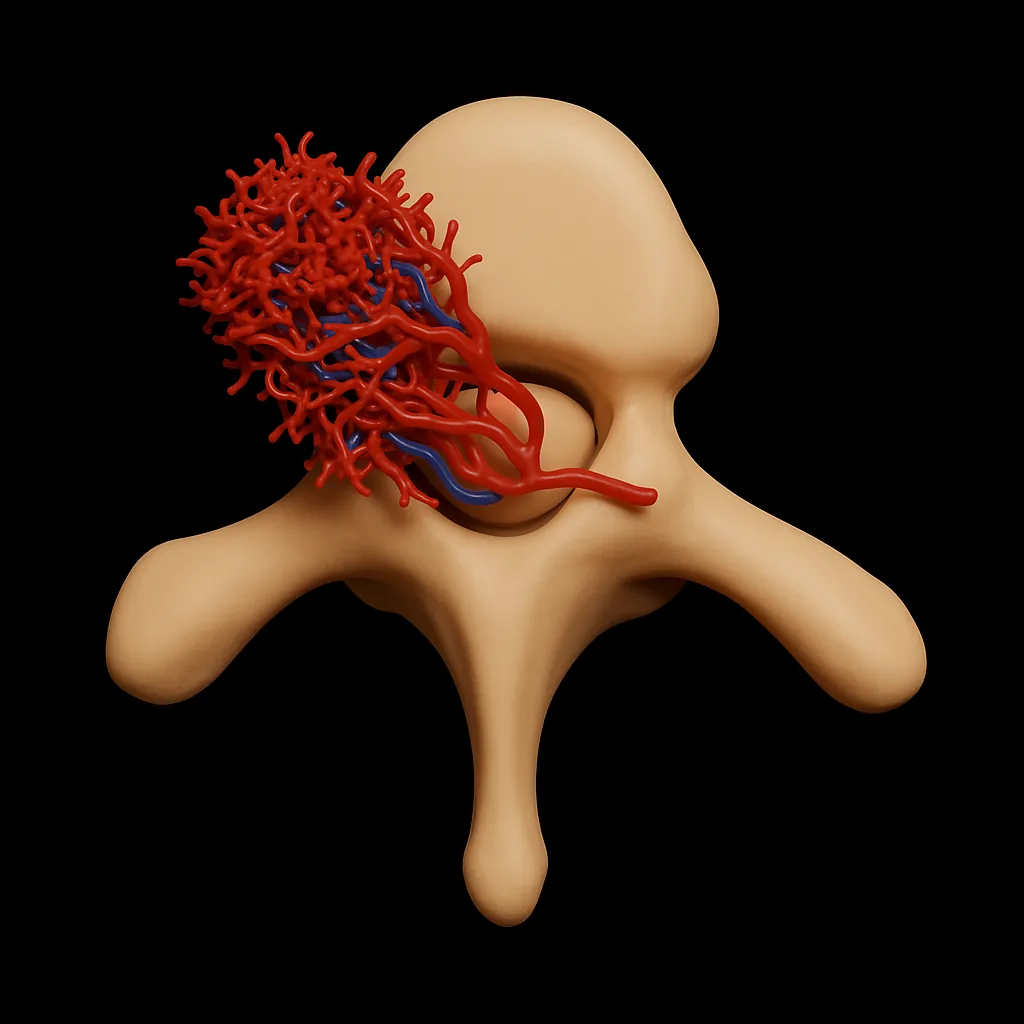
Abnormal vessels of the spinal cord that can cause pain, weakness, or bleeding. Treated with targeted endovascular or surgical care.
Find out more
Raised pressure around the brain that can cause headaches and visual symptoms. Managed with medication, weight management, and selected procedures.
Find out more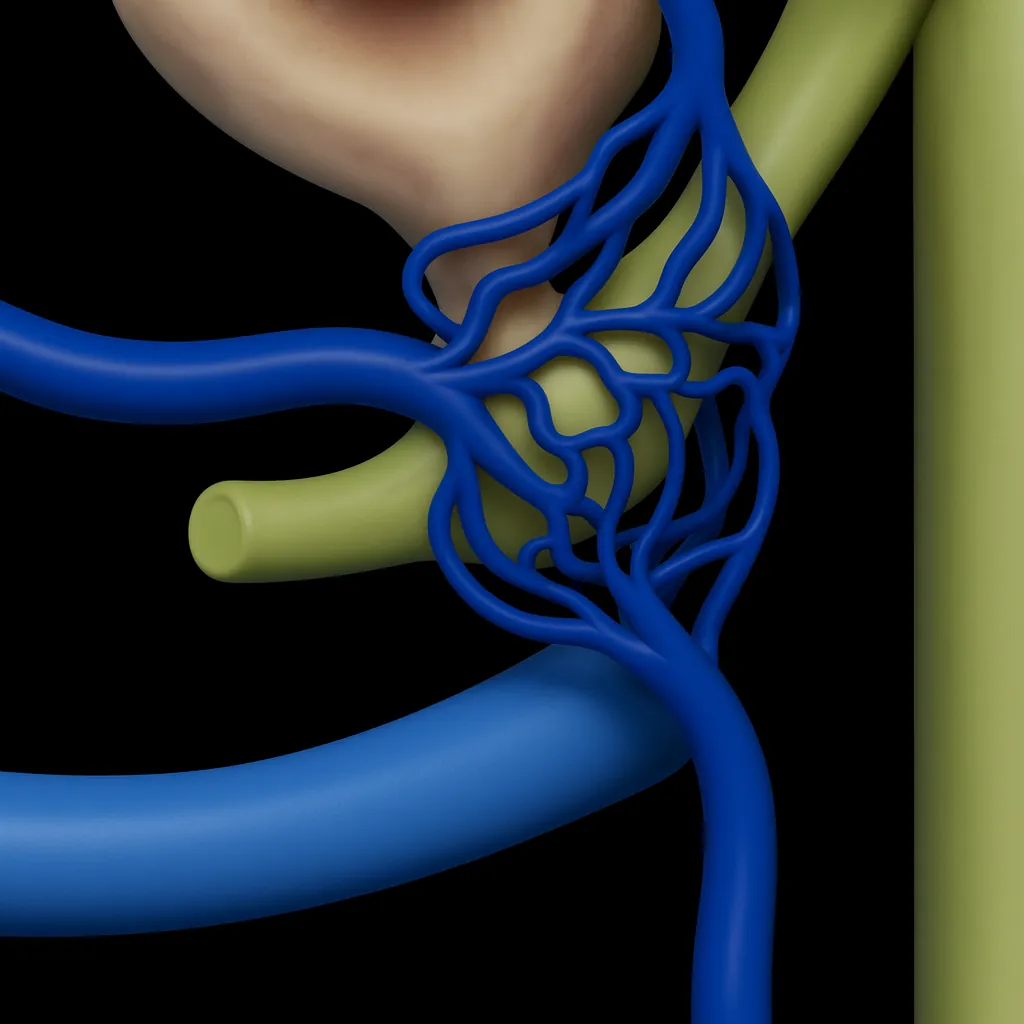
Low pressure in the brain (idiopathic intracranial hypotension) that causes postural headache. Treated with targeted blood patches and repair techniques.
Find out more
A rhythmic sound in the ear often caused by a blood vessel problem. We investigate the cause and offer targeted endovascular treatments.
Find out more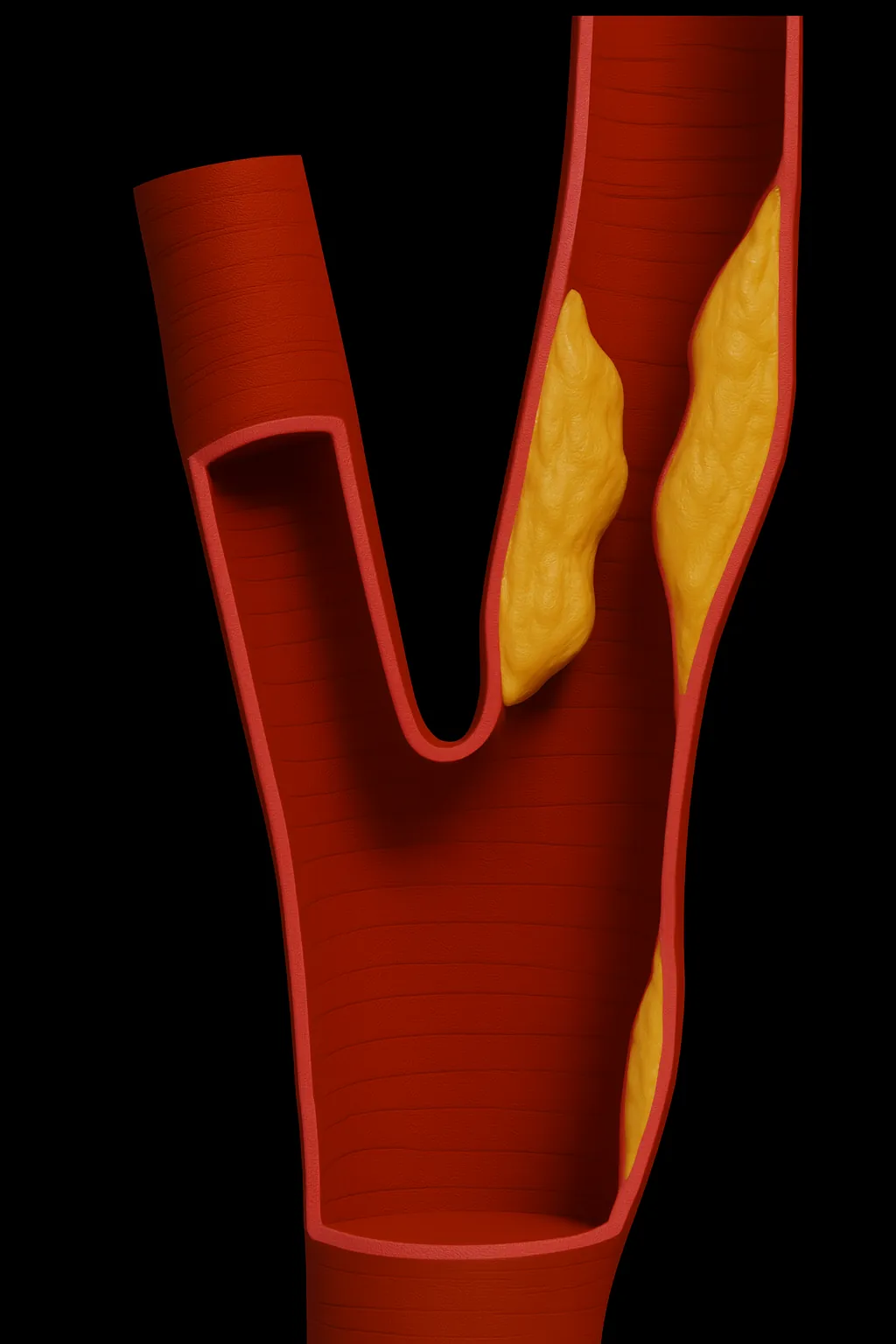
Narrowing of the neck artery that supplies the brain. We assess stroke risk and treat with stenting when appropriate.
Find out more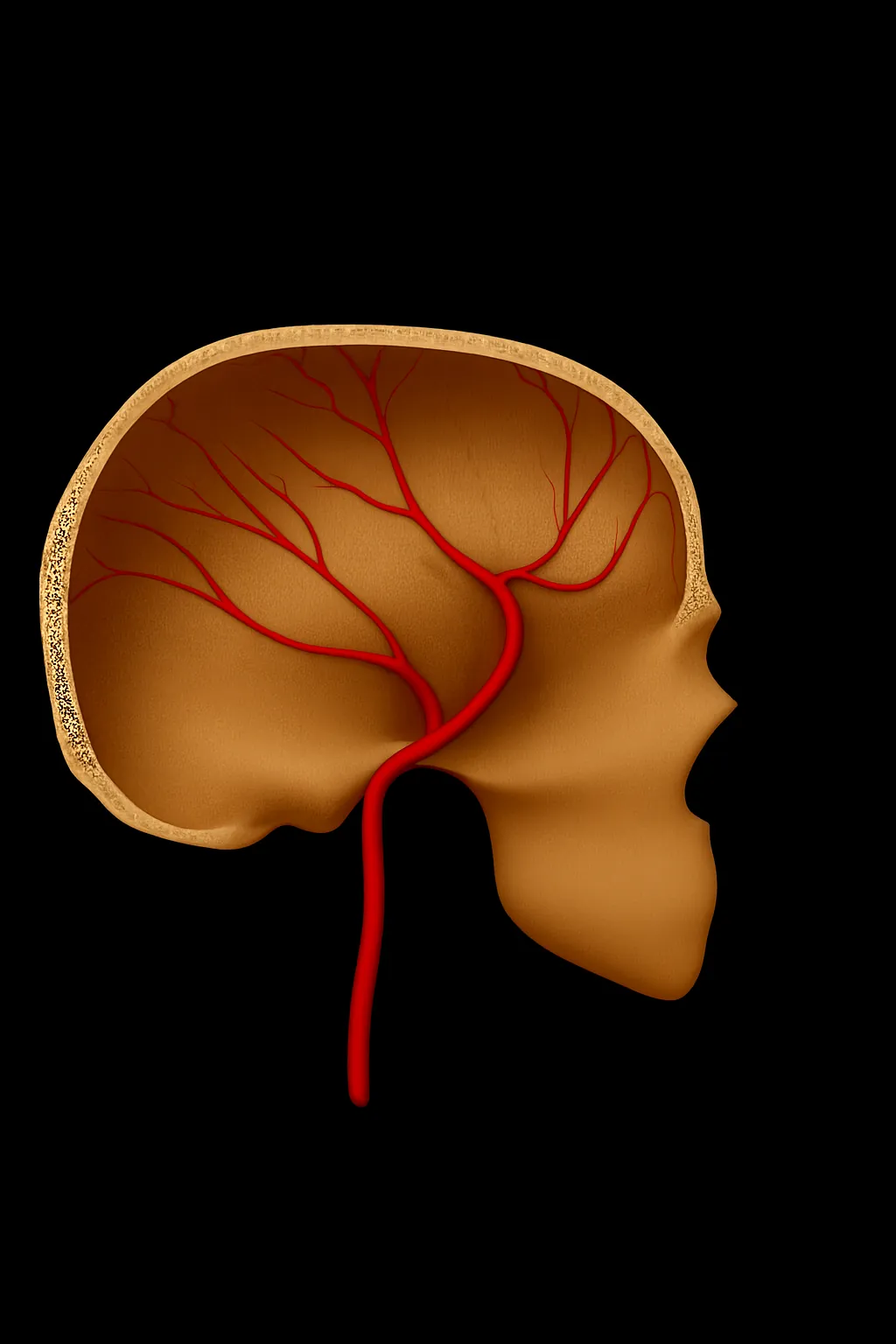
A minimally invasive treatment for chronic subdural haematoma. Tiny particles or liquid close branches of the middle meningeal artery.
Find out more
Fast, detailed X-ray imaging to detect bleeding, strokes, or structural brain problems.
Find out more
High-resolution imaging using magnetic fields, excellent for brain and spine conditions.
Find out more
Gold-standard test using X-rays and contrast dye to show brain blood vessels in detail.
Find out more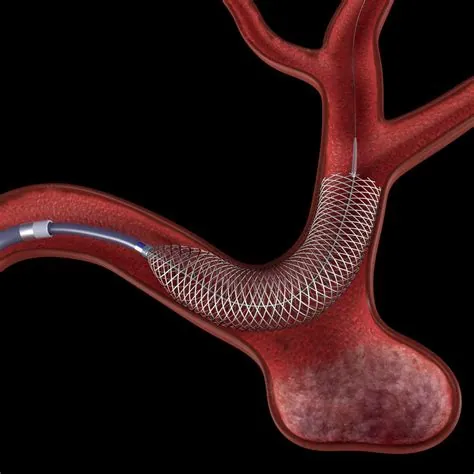
Outlines the main treatment approaches for brain aneurysms, comparing coiling, clipping, and newer devices, and explains how doctors decide which option is best.

Understanding the differences between clipping and coiling for brain aneurysms and how to decide which treatment may be best for you.

Describes the role of lifestyle in preventing aneurysms and bleeds.

Covers what it means to be diagnosed with a brain aneurysm, the risks involved, and what patients can do to stay safe.

Explains the key symptoms of a brain aneurysm rupture, what unruptured aneurysms can cause, and when to seek urgent medical help.

Who should and should not be screened for brain aneurysms?

Are brain aneurysms inevitable or can you reduce your chances?
What to expect from aneurysm treatment, how surgical risks compare with endovascular options, and why many aneurysms are monitored rather than operated on.

What to expect when staying in hospital for treatment of a brain aneurysm.